What are PCB Manufacturing Tolerances?
PCB manufacturing tolerances refer to the acceptable variations in the dimensions, shapes, and positions of the various features on a printed circuit board. These tolerances are necessary due to the limitations of the manufacturing processes and the inherent variability in materials and equipment.
Some common PCB manufacturing tolerances include:
- Trace width and spacing
- Hole size and position
- Solder mask and silkscreen registration
- Board thickness and dimensions
Trace Width and Spacing Tolerances
Trace width and spacing tolerances are crucial for ensuring the proper functioning of a PCB. These tolerances dictate the minimum and maximum allowable widths of the copper traces and the spacing between them.
| Trace Width (mm) | Minimum Spacing (mm) |
|---|---|
| 0.1 – 0.2 | 0.1 |
| 0.2 – 0.3 | 0.15 |
| 0.3 – 0.5 | 0.2 |
| 0.5 – 1.0 | 0.25 |
Table 1: Trace width and minimum spacing tolerances
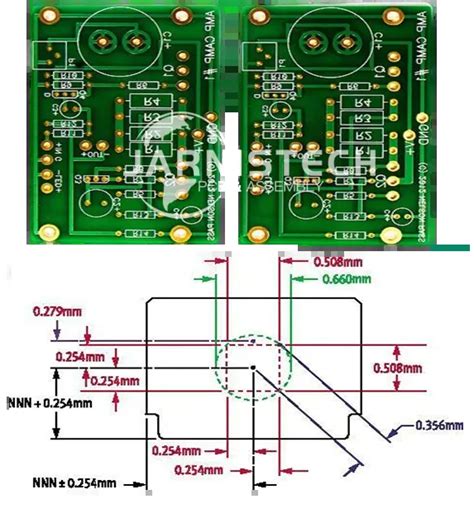
Hole Size and Position Tolerances
Hole size and position tolerances are important for component placement and solderability. These tolerances specify the allowable variations in the diameter of the drilled holes and their position relative to the board’s features.
| Hole Diameter (mm) | Tolerance (mm) |
|---|---|
| 0.3 – 0.5 | ±0.05 |
| 0.5 – 1.0 | ±0.1 |
| 1.0 – 2.0 | ±0.15 |
| 2.0 – 5.0 | ±0.2 |
Table 2: Hole size tolerances
Solder Mask and Silkscreen Registration Tolerances
Solder mask and silkscreen registration tolerances ensure that these layers align properly with the copper features on the PCB. Misalignment can lead to issues such as exposed copper or incorrect component placement.
| Feature | Tolerance (mm) |
|---|---|
| Solder Mask | ±0.05 |
| Silkscreen | ±0.1 |
Table 3: Solder mask and silkscreen registration tolerances
Board Thickness and Dimension Tolerances
Board thickness and dimension tolerances are essential for ensuring that the PCB fits properly in its intended enclosure and aligns with other components in the assembly.
| Board Thickness (mm) | Tolerance (mm) |
|---|---|
| 0.4 – 0.8 | ±0.1 |
| 0.8 – 1.6 | ±0.15 |
| 1.6 – 3.2 | ±0.2 |
Table 4: Board thickness tolerances
Incorporating Fabrication Tolerance Options in Manufacturer Deliverables
To ensure that your PCB meets the required manufacturing tolerances, it is essential to communicate these requirements clearly to your manufacturer. This can be done by incorporating fabrication tolerance options in your manufacturer deliverables.
Gerber Files
Gerber files are the standard format for conveying PCB design information to manufacturers. When generating Gerber files, be sure to include the following tolerance-related information:
- Trace width and spacing
- Hole sizes and positions
- Solder mask and silkscreen apertures
- Board outline and dimensions
Fabrication Drawing
A fabrication drawing is a document that provides additional information and specifications not included in the Gerber files. In your fabrication drawing, specify the following:
- Material type and thickness
- Copper weight
- Surface finish
- Impedance control requirements
- Any special tolerances or requirements
Communication with the Manufacturer
In addition to providing comprehensive deliverables, it is crucial to maintain open communication with your PCB manufacturer. Discuss your tolerance requirements with them and ensure that they can meet these specifications. If there are any concerns or limitations, work with the manufacturer to find suitable solutions or compromises.
FAQ
-
What happens if my PCB design does not meet the manufacturing tolerances?
If your PCB design does not meet the specified manufacturing tolerances, it may lead to issues such as poor component fit, incorrect trace connections, or even complete failure of the board. It is essential to design within the acceptable tolerances to ensure proper functionality and reliability. -
Can I request tighter tolerances than the standard options?
Yes, it is possible to request tighter tolerances than the standard options offered by PCB manufacturers. However, keep in mind that tighter tolerances may increase the manufacturing cost and lead time. Discuss your specific requirements with your manufacturer to determine the feasibility and cost implications. -
How do I determine the appropriate tolerances for my PCB design?
The appropriate tolerances for your PCB design depend on several factors, such as the component sizes, circuit complexity, and the intended application. Consult with your PCB designer and manufacturer to determine the optimal tolerances based on your specific requirements and the capabilities of the manufacturing process. -
What should I do if my manufacturer cannot meet my tolerance requirements?
If your manufacturer cannot meet your tolerance requirements, discuss alternative options or compromises. This may involve redesigning certain aspects of your PCB, using a different manufacturing process, or finding a manufacturer with more advanced capabilities. It is important to find a solution that balances your requirements with the practical limitations of the manufacturing process. -
Can PCB manufacturing tolerances affect the electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) of my device?
Yes, PCB manufacturing tolerances can impact the EMC performance of your device. Variations in trace widths, spacings, and Dielectric Properties can alter the impedance and coupling characteristics of the PCB, potentially leading to EMC issues. It is important to consider EMC requirements when specifying tolerances and to perform appropriate testing to ensure compliance.

Conclusion
PCB manufacturing tolerances are a critical aspect of PCB design and production. By understanding the various tolerances and incorporating them into your manufacturer deliverables, you can ensure that your PCB meets the required specifications and functions as intended. Clear communication with your manufacturer and a comprehensive set of deliverables are key to achieving the best results.
Remember to consider the specific requirements of your application, the capabilities of your chosen manufacturing process, and the potential impact on cost and lead time when specifying tolerances. By striking the right balance and working closely with your manufacturer, you can produce high-quality, reliable PCBs that meet your performance and functionality goals.

Leave a Reply