Introduction to BOM Management for Moisture Sensitive Devices
Effective BOM (Bill of Materials) management is crucial for preventing problems when manufacturing products containing moisture sensitive devices (MSDs). MSDs, such as certain integrated circuits, can be damaged by exposure to humidity during storage and handling. This leads to reliability issues, costly rework, and scrap. Proactively managing the BOM helps identify MSDs and ensures proper storage, handling, and manufacturing processes are in place to protect them.
What are Moisture Sensitive Devices?
Moisture sensitive devices are electronic components prone to damage from absorbed moisture or vapor. Common MSDs include:
- Plastic encapsulated microcircuits (PEMs)
- Semiconductors
- Printed circuit board assemblies
- Printed wiring boards
When exposed to humidity, MSDs can suffer internal delamination, “popcorning” or cracking during reflow soldering. Electrical opens or shorts may also occur. Therefore, MSDs require careful handling, storage, and baking before assembly.
Classification of Moisture Sensitive Devices
Industry standards IPC/JEDEC J-STD-020 and J-STD-033 define eight moisture sensitivity levels (MSLs) for classifying MSDs based on their tolerance for humidity exposure:
| MSL | Max Floor Life |
|---|---|
| 1 | Unlimited |
| 2 | 1 year |
| 2a | 4 weeks |
| 3 | 168 hours |
| 4 | 72 hours |
| 5 | 48 hours |
| 5a | 24 hours |
| 6 | Mandatory bake |
Components with higher MSLs can withstand less exposure time (floor life) before requiring re-baking to remove absorbed moisture.
Importance of BOM Management for Preventing MSD Issues
Identifying MSDs in the BOM
The first step in preventing moisture-related problems is to identify which components in the BOM are MSDs. Suppliers should provide MSD classification data on moisture sensitivity, proper storage conditions, and handling/assembly procedures in accordance with industry standards.
It’s important to capture this MSD data in the BOM or PLM system, so it’s readily accessible. The BOM should include fields for:
- Manufacturer part number
- Moisture sensitivity level (MSL)
- Maximum exposure time (floor life)
- Dry packaging requirements
- Baking parameters (time, temperature)
Planning for MSD Storage and Handling
With MSDs identified in the BOM, planning for proper storage and handling is essential. Key considerations include:
- Dry storage cabinets or desiccant packaging for humidity control
- ESD-safe racks, bags and tools to prevent electrostatic discharge damage
- Tracking exposure time of unsealed MSDs
- Procedures for re-sealing, re-baking exposed parts
- Training personnel on MSD handling methods
Well-managed BOMs facilitate planning by giving full visibility to all MSD parts and their storage/handling requirements.
Avoiding Counterfeit MSD Components
Counterfeit electronic components, including MSDs, are an increasing supply chain risk. Using authentic parts sourced through authorized distributors or directly from OCMs is vital.
Careful BOM management helps screen out counterfeit MSDs by:
- Specifying approved manufacturers and distributors
- Requiring traceability documentation (CoC, CoO, DS, test records)
- Planning for incoming inspection and authenticity testing
- Monitoring for high-risk or obsolete parts that may invite counterfeiting
Monitoring and Control of MSD Parts
BOMs containing MSDs require extra monitoring and control during purchasing, receiving, storage and manufacturing to maintain moisture control.
Some best practices:
– Inspect MSD packaging integrity at receiving
– Record quantities, seal dates, and exposure times
– Segregate MSD inventories by MSL
– Re-bake if floor life will be exceeded before assembly
– Audit MSD handling processes regularly
Leveraging BOM data on MSL levels and floor life limits, along with barcode scanning or RFID tracking, enables tight monitoring and traceability of MSD parts throughout the supply chain.
Implementing BOM Management Solutions for MSDs
ERP/MRP Systems for BOM and Inventory Management
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) and material requirements planning (MRP) systems provide essential BOM management functionality for MSDs. Key capabilities to look for include:
- Ability to store MSD attributes (MSL, floor life, etc.)
- Tracking of MSD inventory quantities by date code, lot code, and location
- Monitoring of exposure times against floor life limits
- Triggers for re-baking or dry storage based on exposure
- Integration with barcode/RFID scanning for warehouse management
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) Systems
PLM systems serve as a central repository for product data, BOMs, design files, and engineering change management across the product lifecycle. PLM benefits for MSD management include:
- Managing manufacturer part data and MSD classifications
- Controlling BOM revisions and alerting for MSD changes
- Workflow tools for ECOs impacting MSDs
- Integration with ERP/MRP systems for seamless data flow
Supply Chain Collaboration Portals
Web-based supplier portals enhance collaboration and data exchange with manufacturers and distributors of MSD components. Through portals, suppliers can:
- Upload MSD classifications, packaging and handling data
- Provide certificates of conformance and analytical test results
- Respond to RFQs and POs, including MSD requirements
- Give advance shipment notices with MSD packaging details
Automating MSD-related communications with the supply base cuts leadtimes, reduces errors and drives adherence to MSD standards.

Training and Education on MSD Management
Employee Training Programs
Effectively managing MSDs requires well-trained employees who understand the risks and follow proper handling procedures. A comprehensive training program should cover:
- MSD types and classification system
- ESD and moisture control methods
- Dry packaging, baking, storage and sealing processes
- Tracking and recording of exposure times
- Corrective actions for moisture exposure events
Regular refresher training and audits reinforce good MSD handling practices.
Supply Chain Partner Education
Suppliers and distributors also play a key role in MSD control. Education initiatives may include:
- Workshops on industry MSD standards
- Training on MSD packaging and labeling requirements
- Scorecards on MSD non-conformances or moisture exposure incidents
- Collaborative problem-solving on chronic MSD issues
Building a shared understanding of MSD risks and mitigation strategies with supply partners improves quality and reliability.
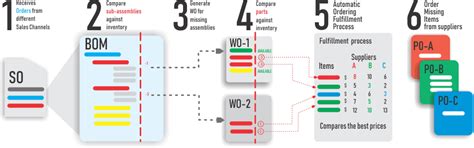
Conclusion
Preventing problems with moisture sensitive devices requires diligent BOM management and close attention to storage, handling and assembly processes. By leveraging BOM management systems to identify and track MSDs, coupled with supplier collaboration and employee training, manufacturers can avoid moisture-related defects that impact product quality and customer satisfaction. Upfront investments in tools and processes for MSD control pay dividends in higher yields, less rework and improved reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What types of components are typically moisture sensitive?
Moisture sensitive devices include plastic encapsulated microcircuits, semiconductors, printed circuit boards, and printed wiring assemblies, among others. Parts with hygroscopic materials that readily absorb moisture are at higher risk.
How do I determine the moisture sensitivity level (MSL) of a component?
Refer to the component manufacturer’s datasheet or contact the supplier directly for the MSL classification based on IPC/JEDEC J-STD-020 and J-STD-033 standards. The MSL rating indicates the floor life or exposure time allowed before re-baking is required.
What happens if a moisture sensitive device exceeds its floor life exposure limit?
If an MSD is exposed to ambient humidity for longer than the specified floor life, it must be baked in a drying oven at the temperature and duration prescribed for its MSL to remove excess moisture before assembly. Otherwise, the part may suffer permanent damage like delamination or cracking during solder reflow.
How should I store moisture sensitive devices to prevent degradation?
MSDs should be stored in a dry environment, either in moisture-barrier bags with desiccant or in humidity-controlled cabinets below 5% RH. Always use caution when handling MSDs and minimize their time out of dry packaging to prevent moisture uptake.
What can I do to prevent problems with moisture sensitive devices in my supply chain?
Effective BOM management is key to identifying and tracking MSDs in your supply chain. Use ERP/MRP and PLM systems to capture MSD classifications and control exposure times. Establish receiving inspection, dry storage, bake-out, and re-sealing processes. Train employees and supply partners on proper MSD storage and handling methods. Consider using supplier collaboration portals for real-time visibility and communications on MSD shipments and requirements.
Leave a Reply