Introduction to FR4 and its Properties
FR4, or Flame Retardant 4, is a widely used glass-reinforced epoxy laminate material in the electronics industry. It is known for its excellent mechanical, electrical, and thermal properties, making it an ideal choice for printed circuit boards (PCBs) and other electronic applications. FR4 is made by combining woven fiberglass cloth with an epoxy resin binder, which is then cured under heat and pressure to form a rigid, stable material.
Composition of FR4
FR4 is composed of two main components:
- Fiberglass cloth: This is a woven fabric made from fine glass fibers, which provides the material with its mechanical strength and dimensional stability.
- Epoxy resin: A thermoset polymer that acts as a binder, holding the fiberglass cloth together and providing electrical insulation and heat resistance.
The combination of these components results in a composite material with a unique set of properties that make it suitable for various applications in the electronics industry.
Manufacturing Process of FR4
The manufacturing process of FR4 involves several steps:
- Impregnation: The fiberglass cloth is impregnated with the epoxy resin, ensuring that the resin fully penetrates the fibers.
- Layup: Multiple layers of the impregnated fiberglass cloth are stacked together to achieve the desired thickness.
- Pressing: The stacked layers are placed in a press, where heat and pressure are applied to cure the epoxy resin and bond the layers together.
- Cutting: The cured laminate is cut to the desired size and shape.
- Finishing: The surface of the laminate may be sanded or polished to achieve a smooth finish, and any necessary holes or features are drilled or machined.
Dielectric Constant of FR4
The dielectric constant, also known as relative permittivity (εr), is a critical property of FR4 that determines its ability to store electrical energy. It is a measure of the material’s capacity to polarize in response to an applied electric field, relative to the permittivity of free space (ε0).
Factors Affecting the Dielectric Constant of FR4
Several factors can influence the dielectric constant of FR4:
- Frequency: The dielectric constant of FR4 varies with the frequency of the applied electric field. As frequency increases, the dielectric constant generally decreases.
- Temperature: Changes in temperature can affect the dielectric constant of FR4. As temperature increases, the dielectric constant typically increases slightly.
- Moisture content: The presence of moisture in FR4 can lead to an increase in its dielectric constant, as water has a higher dielectric constant than the base material.
- Resin composition: The type and proportion of epoxy resin used in the manufacturing process can influence the dielectric constant of FR4.
Typical Dielectric Constant Values for FR4
The dielectric constant of FR4 can vary depending on the specific formulation and manufacturing process used. However, typical values for the dielectric constant of FR4 at various frequencies are as follows:
| Frequency | Dielectric Constant (εr) |
|---|---|
| 1 MHz | 4.5 – 5.0 |
| 10 MHz | 4.4 – 4.9 |
| 100 MHz | 4.3 – 4.8 |
| 1 GHz | 4.2 – 4.7 |
It is important to note that these values are approximate and can vary based on the specific FR4 material and environmental conditions.
Mechanical Properties of FR4
FR4 exhibits excellent mechanical properties, making it suitable for various applications that require structural stability and durability.
Tensile Strength
Tensile strength is a measure of a material’s ability to withstand pulling forces without breaking. FR4 has a high tensile strength, typically ranging from 310 to 380 MPa (45,000 to 55,000 psi) in the warp direction and 280 to 350 MPa (40,000 to 50,000 psi) in the fill direction.
Flexural Strength
Flexural strength, also known as bend strength, is a material’s ability to resist bending under load. FR4 has a flexural strength of approximately 415 to 585 MPa (60,000 to 85,000 psi) in the warp direction and 345 to 485 MPa (50,000 to 70,000 psi) in the fill direction.
Compressive Strength
Compressive strength is a material’s capacity to withstand compression forces without failing. FR4 has a compressive strength of about 415 to 585 MPa (60,000 to 85,000 psi) in both the warp and fill directions.
Impact Strength
Impact strength is a measure of a material’s ability to absorb energy during rapid loading, such as an impact. FR4 has an impact strength of approximately 65 to 95 kJ/m² (30 to 45 ft-lbs/in²) using the Izod notched impact test method.

Thermal Properties of FR4
FR4 is known for its good thermal properties, which make it suitable for use in applications that require heat resistance and stability.
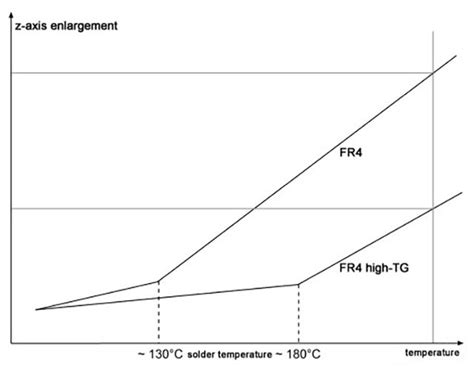
Glass Transition Temperature (Tg)
The glass transition temperature (Tg) is the temperature at which a polymer transitions from a hard, glassy state to a soft, rubbery state. For FR4, the Tg is typically between 130°C and 140°C (266°F to 284°F), depending on the specific formulation.
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE)
The coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) is a measure of how much a material expands or contracts with changes in temperature. FR4 has a CTE of approximately 14 to 16 ppm/°C (7.8 to 8.9 ppm/°F) in the X and Y directions, and 50 to 70 ppm/°C (28 to 39 ppm/°F) in the Z direction.
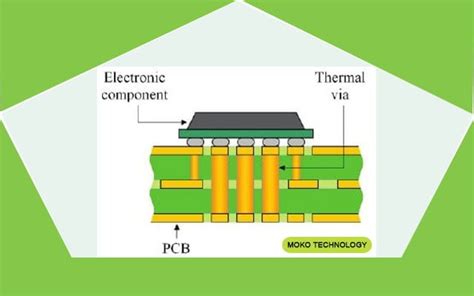
Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity is a material’s ability to conduct heat. FR4 has a relatively low thermal conductivity, typically ranging from 0.3 to 0.4 W/m·K (2.1 to 2.8 Btu·in/hr·ft²·°F), which helps to insulate electronic components and prevent heat buildup.
Electrical Properties of FR4
FR4 is an excellent electrical insulator, making it an ideal choice for PCBs and other electronic applications.
Dielectric Strength
Dielectric strength is a material’s ability to withstand electric fields without breaking down and allowing current to flow. FR4 has a dielectric strength of approximately 20 to 28 kV/mm (500 to 700 V/mil), depending on the thickness and specific formulation.
Volume Resistivity
Volume resistivity is a measure of a material’s resistance to the flow of electrical current through its volume. FR4 has a high volume resistivity, typically in the range of 10¹⁴ to 10¹⁶ Ω·cm.
Surface Resistivity
Surface resistivity is a measure of a material’s resistance to the flow of electrical current across its surface. FR4 has a high surface resistivity, usually in the range of 10¹² to 10¹⁴ Ω/square.
Dissipation Factor (Tan δ)
The dissipation factor, also known as tan δ or loss tangent, is a measure of a material’s ability to dissipate electrical energy as heat. FR4 has a relatively low dissipation factor, typically ranging from 0.02 to 0.03 at 1 MHz, which helps to minimize signal loss and maintain signal integrity in electronic applications.
Applications of FR4
FR4 is widely used in various industries due to its excellent mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties. Some common applications include:
- Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs): FR4 is the most common substrate material for PCBs, providing a stable and reliable platform for electronic components and circuitry.
- Automotive electronics: FR4 is used in automotive electronic systems, such as engine control units, infotainment systems, and sensor modules.
- Aerospace and defense: FR4 is employed in avionics, radar systems, and other military electronics due to its reliability and performance under harsh conditions.
- Industrial equipment: FR4 is used in industrial control systems, power electronics, and automation equipment.
- Consumer electronics: FR4 is found in a wide range of consumer electronic devices, including smartphones, tablets, laptops, and gaming consoles.
Advantages and Disadvantages of FR4
Like any material, FR4 has both advantages and disadvantages that should be considered when selecting it for a specific application.
Advantages
- Excellent mechanical properties, providing structural stability and durability
- Good electrical insulation properties, making it suitable for electronic applications
- High heat resistance and dimensional stability
- Relatively low cost compared to other high-performance materials
- Well-established manufacturing processes and supply chain
Disadvantages
- Limited high-frequency performance due to its relatively high dielectric constant and dissipation factor
- Susceptible to moisture absorption, which can affect its electrical and mechanical properties
- Anisotropic properties, with different characteristics in the X, Y, and Z directions
- Not suitable for extremely high-temperature applications, as it may degrade or lose its properties above its glass transition temperature
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What does FR4 stand for?
-
FR4 stands for Flame Retardant 4, indicating that it is a flame-retardant material with a specific rating.
-
Is FR4 a good insulator?
-
Yes, FR4 is an excellent electrical insulator, making it suitable for use in printed circuit boards and other electronic applications.
-
What is the difference between FR4 and G10?
-
FR4 and G10 are similar materials, both made from glass-reinforced epoxy laminates. However, FR4 is specifically designed to be flame-retardant, while G10 is not. Additionally, FR4 is typically used for electronic applications, while G10 is more commonly used for mechanical and structural applications.
-
Can FR4 be used in high-temperature applications?
-
FR4 can be used in applications with temperatures up to its glass transition temperature (Tg), which is typically between 130°C and 140°C (266°F to 284°F). However, for extremely high-temperature applications above this range, other materials may be more suitable.
-
How does moisture affect FR4?
- Moisture absorption can affect the electrical and mechanical properties of FR4. It can lead to an increase in the dielectric constant, reduction in insulation resistance, and potential dimensional changes or warping. To minimize these effects, FR4 should be stored and used in a controlled environment with proper moisture management techniques.
Conclusion
FR4 is a versatile and widely used glass-reinforced epoxy laminate material that offers excellent mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties. Its high strength, dimensional stability, and electrical insulation capabilities make it an ideal choice for printed circuit boards and various electronic applications across multiple industries.
When selecting FR4 for a specific application, it is essential to consider its dielectric constant, which can vary based on factors such as frequency, temperature, and moisture content. Additionally, understanding its mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties can help ensure that FR4 is the most suitable material for the intended use.
While FR4 has some limitations, such as its relatively high dielectric constant and susceptibility to moisture absorption, its numerous advantages and well-established manufacturing processes continue to make it a popular choice for many applications. As technology advances and new requirements emerge, FR4 will likely remain a key material in the electronics industry, providing reliable performance and stability in a wide range of products and systems.
Leave a Reply