The Need for ECAD-MCAD Integration
As products become more sophisticated, the need for seamless integration between electronic and mechanical design processes becomes increasingly critical. ECAD-MCAD integration allows engineers to:
- Reduce design errors and rework
- Improve product quality and reliability
- Accelerate time-to-market
- Enhance collaboration between electronic and mechanical teams
Key ECAD-MCAD Capabilities
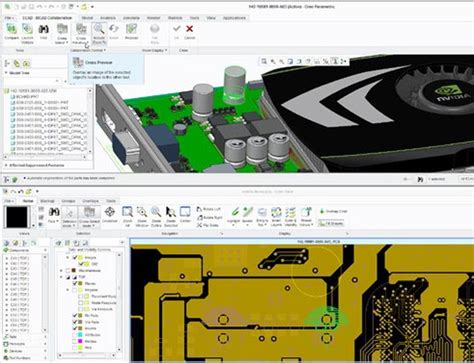
1. 3D Visualization and Collision Detection
One of the most significant benefits of ECAD-MCAD integration is the ability to visualize electronic components within the mechanical enclosure in 3D. This feature allows designers to:
- Identify potential collisions and interferences early in the design process
- Optimize component placement for better heat dissipation and signal integrity
- Ensure proper clearances for assembly and maintenance
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| 3D Visualization | Early identification of design issues |
| Collision Detection | Prevention of costly rework and delays |
2. Real-Time Design Synchronization
Real-time design synchronization ensures that changes made in either the ECAD or MCAD environment are automatically reflected in the other. This capability:
- Eliminates manual data transfer and the associated risk of errors
- Enables concurrent engineering, allowing electronic and mechanical teams to work simultaneously
- Accelerates the design process by reducing the need for manual updates and data exchange
3. Thermal Analysis and Management
Thermal management is critical for ensuring the reliability and performance of electronic products. ECAD-MCAD integration enables engineers to:
- Perform thermal simulations to predict component temperatures and identify hot spots
- Optimize the placement of heat-generating components and cooling solutions
- Validate the effectiveness of thermal management strategies
| Thermal Management Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Heat sinks | Passive cooling devices that dissipate heat from components |
| Fans | Active cooling devices that force air over heat-generating components |
| Thermal interface materials | Materials that enhance heat transfer between components and cooling solutions |
4. Design for Manufacturing (DFM) Analysis
ECAD-MCAD integration enables engineers to perform DFM analysis, ensuring that designs are optimized for manufacturability. This capability allows designers to:
- Identify potential manufacturing issues, such as tight tolerances or difficult-to-assemble components
- Optimize designs for cost-effective manufacturing processes
- Collaborate with manufacturing teams to ensure smooth transition from design to production
5. Bill of Materials (BOM) Management
Integrated ECAD-MCAD systems facilitate the management of BOMs, ensuring that all components are accurately accounted for and properly documented. This feature enables:
- Automatic generation of BOMs based on the latest design data
- Consistency between electronic and mechanical BOMs
- Streamlined procurement and inventory management processes
Case Studies
1. Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace industry, ECAD-MCAD integration has become essential for designing complex avionics systems. By leveraging 3D visualization and collision detection capabilities, engineers can optimize the placement of electronic components within tightly packed avionics bays. Real-time design synchronization ensures that changes made to the electronic design are automatically reflected in the mechanical model, reducing the risk of errors and accelerating the design process.
2. Automotive Industry
The automotive industry relies heavily on ECAD-MCAD integration for designing advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous vehicles. Thermal management is critical for ensuring the reliability of these systems, as they often operate in harsh environments. By performing thermal simulations and optimizing component placement, engineers can ensure that ADAS and autonomous driving systems perform reliably under all conditions.
3. Medical Device Industry
In the medical device industry, ECAD-MCAD integration is crucial for designing compact, highly reliable devices. DFM analysis ensures that designs are optimized for manufacturability, reducing the risk of production delays and quality issues. BOM Management capabilities streamline the procurement process, ensuring that all necessary components are available when needed.

Future Trends in ECAD-MCAD Integration
As technology continues to advance, ECAD-MCAD integration will become even more critical for managing complex designs. Some of the future trends in ECAD-MCAD integration include:
- Increased use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) for design optimization and automation
- Enhanced virtual and augmented reality (VR/AR) capabilities for immersive design experiences
- Greater integration with product lifecycle management (PLM) systems for end-to-end product development
- Improved support for additive manufacturing and other advanced manufacturing processes

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What are the benefits of ECAD-MCAD integration?
ECAD-MCAD integration offers several benefits, including reduced design errors, improved product quality, faster time-to-market, and enhanced collaboration between electronic and mechanical teams.
2. How does 3D visualization help in the design process?
3D visualization allows designers to identify potential collisions and interferences early in the design process, optimize component placement, and ensure proper clearances for assembly and maintenance.
3. What is real-time design synchronization, and why is it important?
Real-time design synchronization ensures that changes made in either the ECAD or MCAD environment are automatically reflected in the other. This eliminates manual data transfer, enables concurrent engineering, and accelerates the design process.
4. How does ECAD-MCAD integration support thermal management?
ECAD-MCAD integration enables engineers to perform thermal simulations, optimize the placement of heat-generating components and cooling solutions, and validate the effectiveness of thermal management strategies.
5. What are some of the future trends in ECAD-MCAD integration?
Future trends in ECAD-MCAD integration include increased use of AI and ML for design optimization, enhanced VR/AR capabilities, greater integration with PLM systems, and improved support for advanced manufacturing processes.
Conclusion
ECAD-MCAD integration has become essential for managing today’s most demanding designs. By leveraging capabilities such as 3D visualization, real-time design synchronization, thermal analysis, DFM analysis, and BOM management, engineers can streamline their workflows, enhance collaboration, and deliver cutting-edge products. As technology continues to advance, ECAD-MCAD integration will play an increasingly critical role in product development, enabling companies to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
[ECAD]: Electronic Computer-Aided Design
[MCAD]: Mechanical Computer-Aided Design
[DFM]: Design for Manufacturing
[BOM]: Bill of Materials
[ADAS]: Advanced Driver Assistance Systems
[AI]: Artificial Intelligence
[ML]: Machine Learning
[VR]: Virtual Reality
[AR]: Augmented Reality
[PLM]: Product Lifecycle Management
Leave a Reply