Category: Printed Circuit Board
-
What does a PCB stand for?
•
The History of Printed Circuit Boards Early Developments The concept of printed circuit boards can be traced back to the early 20th century. In 1903, Albert Hanson, a German inventor, filed a patent for a method of creating an electrical connection by bonding wire to a flat surface. This laid…
-
What is PCB and explain it?
•
Introduction to PCB A Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is a fundamental component in modern electronic devices. It is a flat board made of insulating material, usually fiberglass or composite epoxy, with conductive copper traces printed on its surface. These traces connect various electronic components, such as resistors, capacitors, integrated circuits…
-

What PCB means?
•
What is the Definition of PCB? PCB stands for Printed Circuit Board. It is a thin board made of fiberglass or other composite material, with conductive pathways etched or printed onto the surface. These pathways, also known as traces, connect various electronic components such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits…
-

What is a PCB in engineering?
•
Introduction to Printed Circuit Boards In the world of electronics and engineering, Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) play a crucial role in the functionality and performance of various devices. A PCB is a flat board made of insulating material, such as fiberglass or plastic, with conductive pathways etched or printed onto…
-

How does a PCB work?
•
Introduction to PCB Functionality A Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is a fundamental component in modern electronics. It is a thin board made of fiberglass or other composite material, with conductive pathways etched or printed onto its surface. These pathways, known as traces, connect various electronic components such as resistors, capacitors,…
-
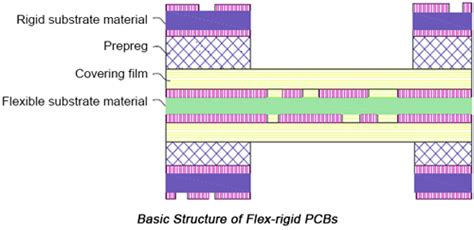
Rigid Flex PCB Design Guidelines and Manufacturing
•
Introduction to Rigid Flex PCBs Rigid flex PCBs combine rigid and flexible substrates into a single integrated assembly. It merges circuitry-laden rigid boards with dynamic flexing elements enabled by flexible materials. They deliver connectivity between multiple rigid electronics subassemblies in complex devices where space efficiencies and high interconnectivity are critical…
-
High-Density Interconnect (HDI) PCB Design and Manufacturing You Need Know
•
What is HDI PCB? HDI (High-Density Interconnect) PCBs are printed circuit boards (PCBs) with a higher wiring density than conventional PCBs. HDI PCBs contain microvias – small vias with diameters under 0.15mm connecting two or more conductive layers. The use of microvias allows trace pitches under 8 mil, increasing circuit…
-
High Frequency PCB: Design, Materials, Manufacturing and Cost
•
High frequency printed circuit boards (PCBs) are designed to operate at high frequencies, typically in the RF (radio frequency) and microwave bands from 300 MHz to 300 GHz. They enable the transmission of high frequency signals in devices and components used for wireless communications, radars, satellite equipment, medical devices and…
-
What Is the Difference Between PCBA and PCB?
•
Introduction Printed Circuit Boards (PCB) What Are PCBs? PCB Materials PCB Design and Fabrication Types of PCBs Printed Circuit Board Assemblies (PCBAs) What are PCBAs? PCBA Fabrication Types of Components Testing PCBAs Key Differences Summarized PCB PCBA Bare board without components Board with components soldered on Focus on interconnects and…