Category: Printed Circuit Board
-
What is ceramic PCB
•
Advantages of Ceramic PCBs 1. High Temperature Resistance One of the most significant advantages of ceramic PCBs is their ability to withstand high temperatures. While standard FR-4 PCBs can typically operate at temperatures up to 130°C, ceramic PCBs can function at temperatures exceeding 260°C. This makes them suitable for applications…
-
How to Manufacture small circuit board
•
Introduction to PCB Manufacturing Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the backbone of modern electronics. They are used in almost every electronic device, from smartphones and computers to medical equipment and aerospace systems. PCBs provide a platform for electrical components to be mounted and connected, allowing for the creation of complex…
-
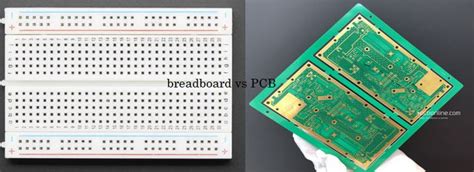
What s The Difference Between PCB And Breadboard
•
What is a PCB? A PCB, or Printed Circuit Board, is a flat board made of insulating material, typically fiberglass or composite epoxy, with conductive copper traces printed onto its surface. These traces are designed to interconnect electronic components, such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits (ICs), according to a…
-
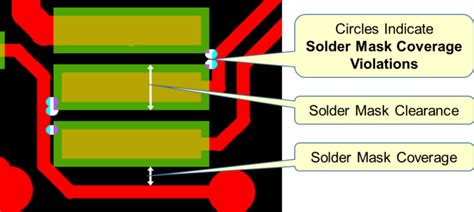
How is solder mask applied on PCB
•
What is Solder Mask and Why is it Important? Solder mask, also known as solder resist or solder stop mask, is a thin layer of polymer that is applied to the copper traces of a printed circuit board (PCB). The primary purpose of solder mask is to protect the copper…
-

How Much PCB Mask Expansion is Too Much?
•
Understanding PCB Mask Expansion PCB mask expansion, also known as solder mask expansion or solder mask overdraw, is a crucial aspect of printed circuit board (PCB) design and manufacturing. It refers to the additional area of solder mask that extends beyond the copper pad on a PCB. This expansion helps…
-
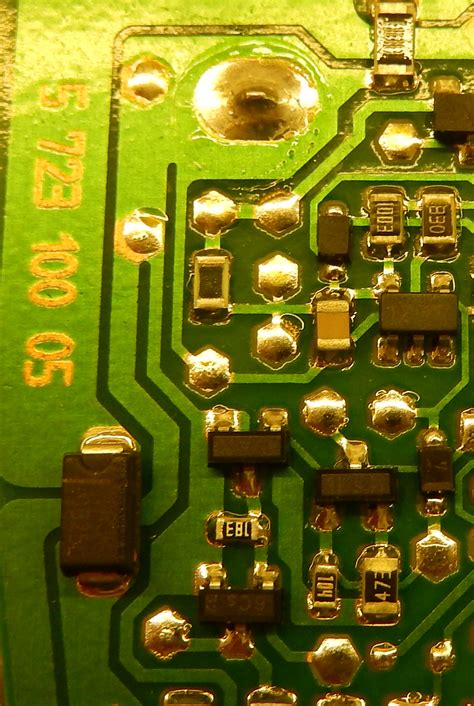
PCB Trace Everything You Need To Know
•
What is a PCB Trace? A PCB trace, also known as a copper trace or circuit trace, is a thin strip of copper that carries electrical signals between components on a printed circuit board (PCB). These traces are essential for the proper functioning of electronic devices, as they provide the…
-
What Is The Difference Between Solder Mask And Solder Paste
•
What is Solder Mask? Solder mask, also known as solder resist or solder stop, is a protective coating applied to the copper traces of a PCB. Its primary purpose is to prevent accidental short circuits and protect the copper from oxidation and other environmental factors. Solder mask is typically applied…
-
3D Printing Circuit Boards for Fast Prototyping
•
Introduction to Circuit Board Prototyping Circuit board prototyping is a critical part of the electronics design process. Before committing to a final printed circuit board (PCB) design for mass production, engineers need to test and validate their designs through prototypes. Traditionally, PCB prototypes have been fabricated using subtractive manufacturing methods…
-
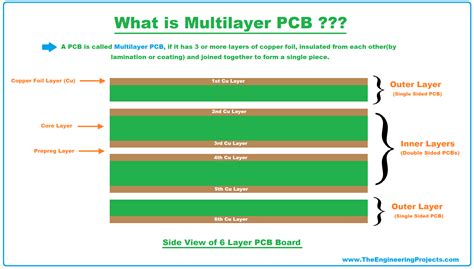
What Is Single Layer PCB
•
Introduction to Single-Layer PCB A Single-Layer PCB, also known as a single-sided PCB, is a printed circuit board that has only one layer of conductive material, typically copper, on one side of the insulating substrate. This layer is used for both signal traces and component pads. Single-Layer PCBs are the…
-
Understanding the PCB Fabrication Process
•
What is PCB Fabrication? PCB fabrication is the process of creating a printed circuit board from a design layout. It involves a series of steps that transform a raw substrate material, typically a copper-clad laminate, into a functional PCB with conductive traces, pads, and other features. The fabrication process requires…