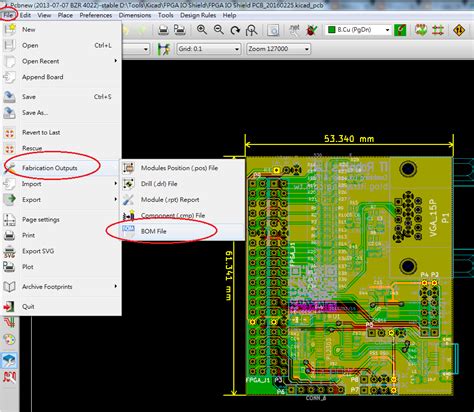
What is a PCB BOM?
A PCB BOM is a comprehensive list of all the components, materials, and quantities required to manufacture a printed circuit board. It serves as a blueprint for the PCB assembly process, guiding manufacturers in sourcing the correct components and ensuring that the final product meets the intended design specifications.
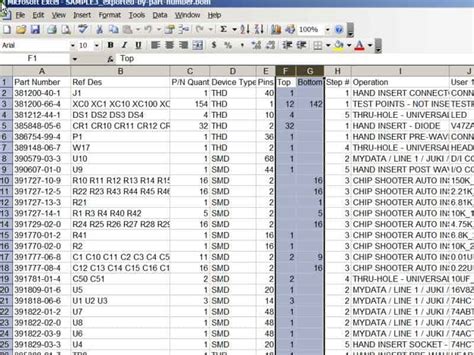
A typical PCB BOM includes the following information:
- Component reference designators
- Manufacturer part numbers
- Descriptions
- Quantities
- Package types
- Supplier information
Maintaining an accurate and up-to-date PCB BOM is essential for several reasons:
- It ensures that the correct components are ordered and used in the manufacturing process.
- It helps in identifying potential supply chain issues and allows for proactive management of component availability.
- It facilitates communication between design teams, procurement, and manufacturing departments.
- It enables better inventory management and cost control.
The Challenges of PCB BOM Management
Managing a PCB BOM can be a complex and time-consuming task, especially for products with a large number of components or frequent design changes. Some of the common challenges include:
-
Inconsistent data: BOMs created by different team members or departments may have inconsistencies in formatting, naming conventions, or data accuracy.
-
Manual data entry: Manually entering and updating BOM data is prone to human error and can be time-consuming.
-
Version control: Keeping track of multiple versions of a BOM and ensuring that all stakeholders are working with the most up-to-date information can be difficult.
-
Component obsolescence: As technology advances, components may become obsolete, requiring updates to the BOM and potentially leading to redesigns.
-
Supply chain disruptions: Unexpected events such as natural disasters, geopolitical issues, or supplier failures can disrupt the supply chain and impact the availability of components listed in the BOM.
To overcome these challenges, manufacturers can leverage various BOM management tools that streamline the process, improve data accuracy, and enhance collaboration between teams.
Types of BOM Management Tools
There are several types of BOM management tools available, each with its own features and benefits. Some of the most common categories include:
1. Spreadsheet-based Tools
Spreadsheet software, such as Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets, is often used for creating and managing BOMs due to its accessibility and familiarity. These tools allow users to enter component data, perform calculations, and format the BOM according to their needs.
Advantages:
– Low cost and readily available
– Flexible and customizable
– Easy to learn and use
Disadvantages:
– Limited version control and collaboration features
– Prone to human error and data inconsistencies
– Difficulty in managing large and complex BOMs
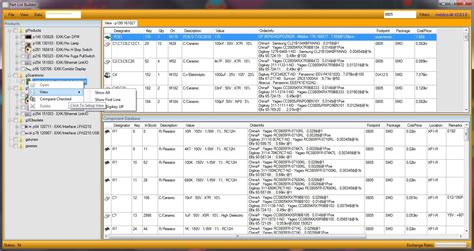
2. Dedicated BOM Management Software
Dedicated BOM management software is specifically designed to handle the unique requirements of creating, maintaining, and sharing BOMs. These tools often include features such as version control, user access control, and integration with other systems such as ERP or PLM.
Examples of dedicated BOM management software include:
- OpenBOM
- Arena BOM
- Aligni
- Altium Vault
Advantages:
– Purpose-built for BOM management
– Robust version control and collaboration features
– Integration with other engineering and manufacturing systems
– Automated data validation and consistency checks
Disadvantages:
– Higher cost compared to spreadsheet-based tools
– May require additional training and implementation time
– Limited customization options compared to spreadsheets
3. PLM-Integrated BOM Management
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) systems are comprehensive solutions that manage the entire lifecycle of a product, from concept to retirement. Many PLM systems include built-in BOM management capabilities, allowing users to create, maintain, and share BOMs within the context of the overall product development process.
Examples of PLM systems with BOM management features include:
- Siemens Teamcenter
- PTC Windchill
- Dassault Systèmes ENOVIA
- Oracle Agile PLM
Advantages:
– Seamless integration with other PLM functionalities, such as CAD, change management, and document control
– Enables a single source of truth for product data
– Supports collaborative workflows and data sharing across the organization
Disadvantages:
– High cost and complexity of implementation
– Requires significant organizational commitment and resources
– May be overkill for small-scale PCB manufacturing operations
4. ERP-Integrated BOM Management
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are designed to manage various business processes, including accounting, procurement, and manufacturing. Some ERP systems offer BOM management capabilities as part of their manufacturing module, enabling users to create and maintain BOMs in the context of the overall production process.
Examples of ERP systems with BOM management features include:
- SAP
- Oracle NetSuite
- Microsoft Dynamics 365
- Epicor
Advantages:
– Integration with other ERP functionalities, such as inventory management, purchasing, and production planning
– Enables a unified view of the manufacturing process
– Supports cost tracking and financial analysis
Disadvantages:
– Complexity and high cost of implementation
– May require customization to meet specific PCB manufacturing requirements
– Limited flexibility compared to dedicated BOM management tools

Key Features to Look for in a BOM Management Tool
When selecting a BOM management tool for PCB manufacturing, consider the following key features:
-
Ease of use: The tool should have a user-friendly interface that allows for easy creation, editing, and sharing of BOMs.
-
Data validation: Automatic data validation features can help ensure the accuracy and consistency of BOM data, reducing the risk of errors.
-
Version control: Robust version control capabilities enable users to track changes, compare different versions, and revert to previous versions if needed.
-
Collaboration: The ability to share BOMs and collaborate with team members in real-time can streamline communication and improve efficiency.
-
Integration: Integration with other engineering and manufacturing systems, such as CAD, ERP, or PLM, can provide a seamless flow of data and reduce manual data entry.
-
Customization: Flexibility to customize fields, templates, and workflows to meet specific PCB manufacturing requirements.
-
Reporting and analytics: Built-in reporting and analytics features can provide valuable insights into BOM data, component usage, and cost trends.
Implementing a BOM Management Tool
Once you have selected a BOM management tool that meets your PCB manufacturing needs, the next step is to implement it effectively. Here are some best practices to follow:
-
Define BOM standards: Establish clear standards for BOM creation, including naming conventions, data formats, and required fields. This will ensure consistency and ease of use across the organization.
-
Train users: Provide comprehensive training to all users who will be interacting with the BOM management tool, including designers, engineers, procurement staff, and production personnel.
-
Integrate with existing systems: Ensure that the BOM management tool is properly integrated with other relevant systems, such as CAD, ERP, or PLM, to enable seamless data flow and avoid duplication of effort.
-
Establish workflows: Define clear workflows for BOM creation, review, approval, and release to manufacturing. This will help streamline the process and ensure that all necessary steps are followed.
-
Monitor and optimize: Regularly monitor the usage and performance of the BOM management tool, and seek feedback from users. Continuously optimize the tool and associated processes based on user input and evolving business needs.
The Future of BOM Management in PCB Manufacturing
As PCB manufacturing continues to evolve, so too will the tools and technologies used to manage BOMs. Some of the emerging trends and developments in BOM management include:
-
Cloud-based solutions: Cloud-based BOM management tools offer increased accessibility, scalability, and collaboration capabilities, enabling teams to work together seamlessly across different locations and devices.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML technologies can be leveraged to automate BOM creation, validation, and optimization processes, reducing manual effort and improving data accuracy.
-
Internet of Things (IoT) integration: As more devices become connected through the IoT, BOM management tools may increasingly incorporate real-time data from sensors and other sources to enable more dynamic and responsive manufacturing processes.
-
Blockchain technology: Blockchain-based BOM management solutions can provide increased security, traceability, and transparency in the supply chain, enabling more efficient and trustworthy collaboration between manufacturers and suppliers.
By staying abreast of these developments and continually evaluating and updating their BOM management tools and practices, PCB manufacturers can position themselves for success in an increasingly competitive and technology-driven industry.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What is the difference between a PCB BOM and a regular BOM?
A PCB BOM is specifically designed for the manufacture of printed circuit boards and includes components, materials, and quantities unique to PCB assembly. A regular BOM, on the other hand, is a more general term that can refer to a bill of materials for any type of product or assembly. -
Can I use a spreadsheet to manage my PCB BOM?
Yes, spreadsheets like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets can be used to manage PCB BOMs, especially for smaller-scale projects. However, as the complexity and size of the BOM grows, dedicated BOM management tools may be more suitable due to their advanced features and capabilities. -
How often should I update my PCB BOM?
Your PCB BOM should be updated whenever there are changes to the design, components, or quantities required for manufacturing. It is essential to keep the BOM as up-to-date as possible to ensure accurate production and avoid delays or errors. -
What should I do if a component in my PCB BOM becomes obsolete?
If a component in your PCB BOM becomes obsolete, you should first try to find a suitable replacement that meets the same functional and technical requirements. If a direct replacement is not available, you may need to redesign the PCB to accommodate an alternative component. Be sure to update the BOM accordingly and communicate the changes to all relevant stakeholders. -
How can I ensure the accuracy of my PCB BOM?
To ensure the accuracy of your PCB BOM, follow these best practices: - Establish clear standards and guidelines for BOM creation and maintenance
- Use automated data validation tools to check for errors and inconsistencies
- Regularly review and update the BOM to reflect any changes in design or components
- Collaborate with suppliers and manufacturers to verify component information and availability
- Implement version control to track changes and maintain a single source of truth
By implementing the right BOM management tools and following best practices, PCB manufacturers can streamline their production processes, reduce errors and delays, and ultimately deliver high-quality products to their customers.
Leave a Reply