What are Aluminum PCBs?
Aluminum PCBs, also known as metal core PCBs (MCPCBs), are printed circuit boards that use aluminum as the base material instead of the traditional FR-4 fiberglass. The aluminum substrate provides excellent thermal conductivity, allowing heat to dissipate quickly from electronic components. This makes aluminum PCBs ideal for applications that generate significant amounts of heat, such as high-power LEDs, automotive electronics, and power converters.
Key Features of Aluminum PCBs
- High thermal conductivity
- Lightweight and durable
- Excellent mechanical stability
- Good electrical insulation
- Cost-effective solution for heat management
Advantages of Using Aluminum PCBs
Superior Heat Dissipation
One of the primary advantages of using aluminum PCBs is their ability to dissipate heat efficiently. The thermal conductivity of aluminum is significantly higher than that of FR-4, as shown in the table below:
| Material | Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) |
|---|---|
| Aluminum | 205 – 250 |
| FR-4 | 0.3 – 0.4 |
This means that aluminum PCBs can transfer heat away from electronic components much more effectively, preventing overheating and ensuring optimal performance.
Lightweight and Durable
Aluminum PCBs are lighter than their FR-4 counterparts, making them suitable for applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in aerospace and automotive industries. Despite being lightweight, aluminum PCBs are highly durable and can withstand harsh environmental conditions, such as high temperatures, vibrations, and shocks.
Cost-Effective Heat Management Solution
Using aluminum PCBs can be a cost-effective solution for managing heat in electronic devices. By efficiently dissipating heat, aluminum PCBs can help reduce the need for additional cooling components, such as heatsinks and fans, which can add to the overall cost of the device. Additionally, the increased thermal efficiency can lead to improved reliability and longer product life, reducing maintenance and replacement costs.
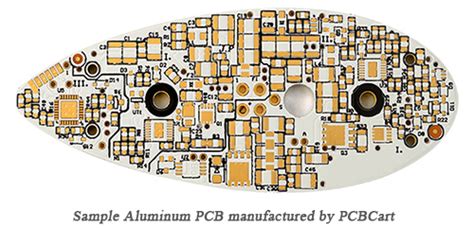
Applications of Aluminum PCBs
High-Power LEDs
Aluminum PCBs are widely used in high-power LED applications, such as automotive lighting, architectural lighting, and outdoor displays. The excellent thermal conductivity of aluminum helps to prevent the LEDs from overheating, which can cause a decrease in luminous efficiency and a shorter lifespan.
Automotive Electronics
The automotive industry relies heavily on aluminum PCBs for various applications, including engine control units (ECUs), power inverters, and battery management systems. The ability of aluminum PCBs to withstand high temperatures and vibrations makes them ideal for the demanding conditions found in automotive environments.
Power Converters
Aluminum PCBs are commonly used in power converters, such as DC-DC converters and AC-DC power supplies. The efficient heat dissipation provided by aluminum PCBs helps to maintain the performance and reliability of these devices, even under high-power loads.

Designing with Aluminum PCBs
Thermal Management Considerations
When designing with aluminum PCBs, it is essential to consider the thermal management aspects of the design. This includes:
- Selecting the appropriate aluminum substrate thickness
- Optimizing the layout of components for efficient heat dissipation
- Using thermal vias to transfer heat from the components to the aluminum substrate
- Incorporating additional cooling methods, such as heatsinks or fans, if necessary
Insulation and Dielectric Materials
To ensure proper electrical insulation between the aluminum substrate and the copper traces, a dielectric layer is used. The most common dielectric materials for aluminum PCBs are:
- Epoxy resin
- Polyimide
- Thermal conductive ceramic
The choice of dielectric material depends on the specific application requirements, such as the operating temperature range, electrical properties, and mechanical properties.
Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process for aluminum PCBs is similar to that of traditional FR-4 PCBs, with a few key differences:
- The aluminum substrate is cleaned and prepared for the application of the dielectric layer.
- The dielectric layer is applied to the aluminum substrate using methods such as screen printing, roller coating, or lamination.
- The copper layer is then applied to the dielectric layer using techniques such as electroplating or foil lamination.
- The desired circuit pattern is created on the copper layer using standard PCB fabrication processes, such as photolithography and etching.
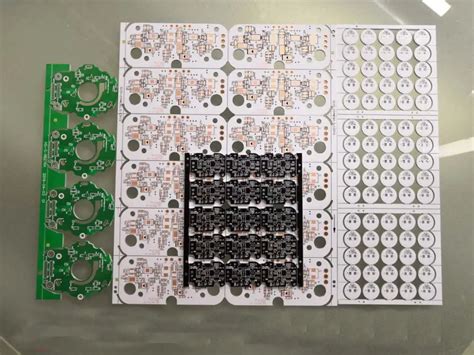
RAYPCB’s Expertise in Aluminum PCBs
RAYPCB is a leading manufacturer of high-quality aluminum PCBs, with years of experience in designing and producing custom solutions for various industries. Our state-of-the-art facilities and skilled technicians ensure that every aluminum PCB meets the highest standards of quality and reliability.
We offer a wide range of aluminum PCB options, including:
- Single-layer and multi-layer designs
- Various aluminum substrate thicknesses
- Different dielectric materials to suit specific application needs
- Custom sizes and shapes
Our team of experts works closely with clients to understand their unique requirements and provide tailored solutions that optimize thermal management and overall performance.
FAQ
1. What is the difference between aluminum PCBs and traditional FR-4 PCBs?
Aluminum PCBs use an aluminum substrate as the base material, while FR-4 PCBs use a fiberglass-reinforced epoxy laminate. The key difference is that aluminum PCBs have much higher thermal conductivity, allowing for better heat dissipation from electronic components.
2. Can aluminum PCBs be used for all electronic applications?
While aluminum PCBs offer excellent thermal management properties, they may not be suitable for all electronic applications. Factors such as cost, weight, and electrical requirements should be considered when deciding whether to use an aluminum PCB or a traditional FR-4 PCB.
3. How do I select the appropriate aluminum substrate thickness for my application?
The choice of aluminum substrate thickness depends on several factors, including the power dissipation requirements, the size and weight constraints, and the mechanical stability needed. Generally, thicker aluminum substrates provide better thermal conductivity and mechanical stability, but they also increase the overall weight and cost of the PCB.
4. Are there any special considerations when designing circuits for aluminum PCBs?
Yes, when designing circuits for aluminum PCBs, it is important to consider the thermal management aspects of the design. This includes optimizing the layout of components for efficient heat dissipation, using thermal vias to transfer heat from the components to the aluminum substrate, and incorporating additional cooling methods if necessary.
5. How do I choose the right dielectric material for my aluminum PCB application?
The choice of dielectric material for an aluminum PCB depends on the specific application requirements, such as the operating temperature range, electrical properties, and mechanical properties. Common dielectric materials include epoxy resin, polyimide, and thermal conductive ceramic. It is best to consult with an experienced aluminum PCB manufacturer, like RAYPCB, to determine the most suitable dielectric material for your application.
Leave a Reply